离子共价(ionic covalent)和金属键(metallic bonds)的区别
主要差异离子(main difference ionic) vs. 共价的(covalent)
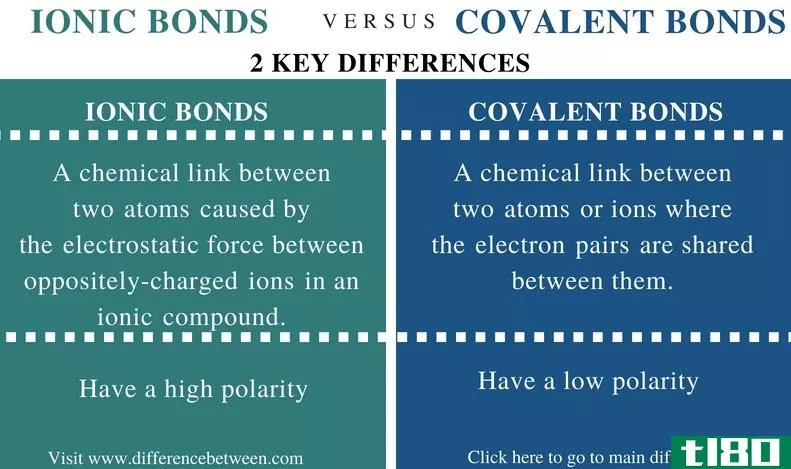
债券可分为两大类;一级债券和次级债券。主键是将原子固定在分子中的化学键,而二次键则是将分子结合在一起的力。主要有三种类型的键,即离子键、共价键和金属键。二次键包括色散键、偶极键和氢键。一次键具有较高的键能,与二次力相比,它更稳定。离子共价键与金属键的主要区别在于它们的形成;当一个原子向另一个原子提供电子时,离子键形成,而当两个原子在金属晶格**享可变数量的电子时,两个原子共享价电子和金属键时形成共价键。
本文探讨,
1.什么是离子键?–定义、形成、性质
2.什么是共价键?–定义、形成、性质
3.什么是金属键?–定义、形成、性质
4. What is the difference between Ionic Covalent and Metallic Bonds?
什么是离子键(ionic bonds)?
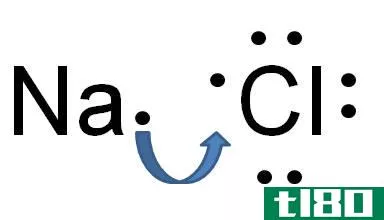
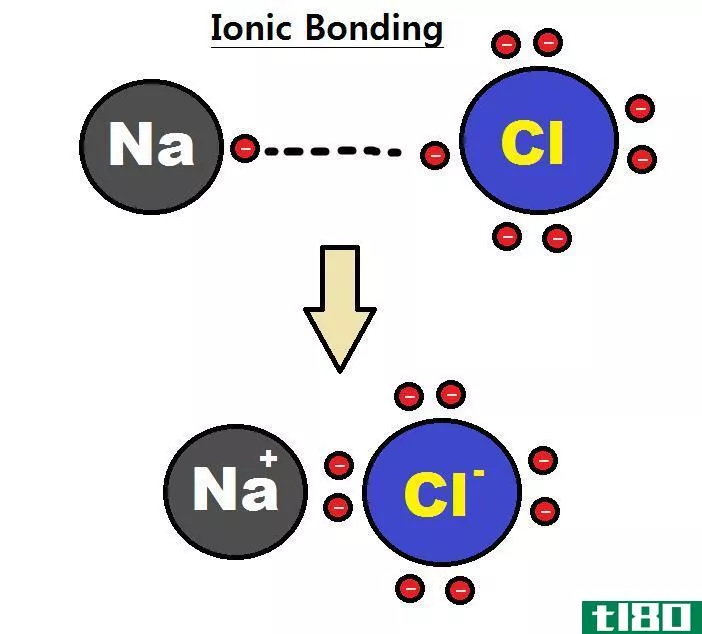
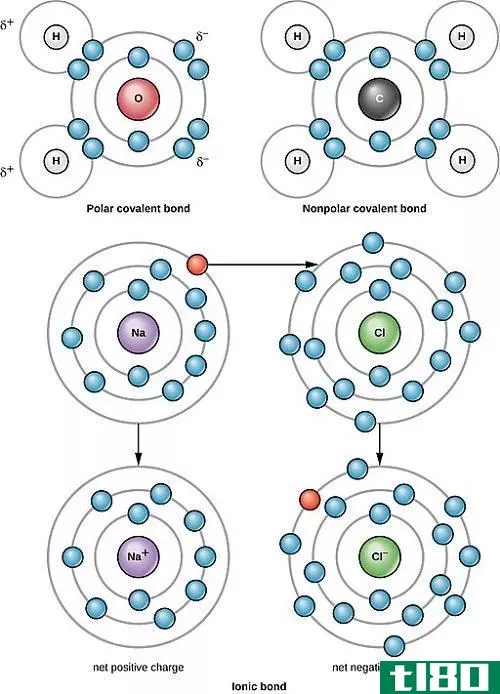
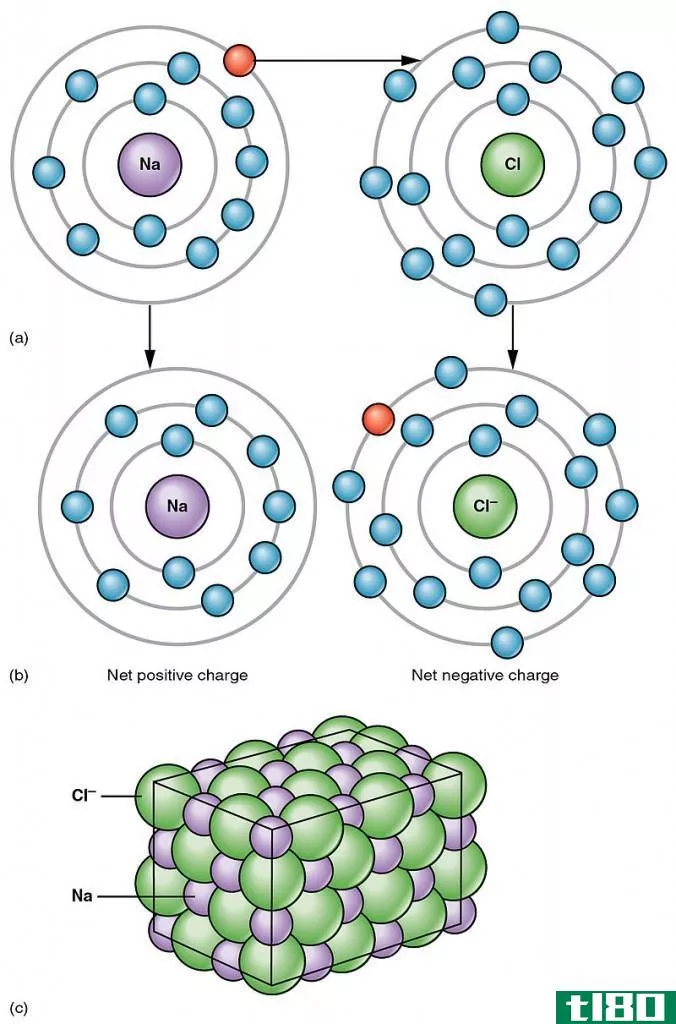
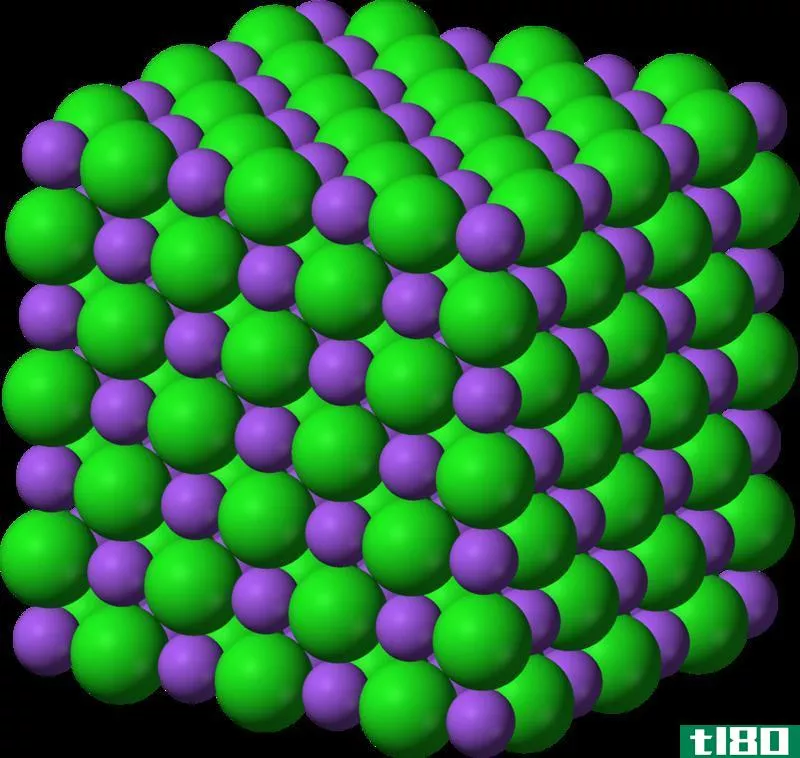
Certain atoms tend to donate or receive electr*** in order to become more stable by completely occupying their outermost orbit. Atoms with very few electr*** in their outermost shell tend to donate the electr*** and become positively charged i***, while atoms with more electr*** in their outermost orbit have a tendency to receive electr*** and become positively charged i***. When these i*** are brought together, the attraction forces are occurred due to opposite charges of i***. These forces are called ionic bonds. These stable bonds are also called electrostatic bonds. Solids bonded with ionic bonds have crystalline structures and low electrical conductivity, which is due to lack of free moving electr***. Bonds usually occur between metal and non-metal that are having a large difference in electronegativity. Examples of ionically bonded materials include LiF, NaCl, BeO, CaF2 etc.
什么是共价键(covalent bonds)?
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share their valence electr***. The two atoms have a **all difference in electronegativity. Covalent bonds occur between same atoms or different types of atoms. For example, fluorine needs one electron to complete its outer shell, thus, one electron is shared by another fluorine atom by making a covalent bond resulting F2 molecule. Covalently bonded materials are found in all three states; i.e., solid, liquid and gas. Examples of covalently bonded material include hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, water molecules, diamond, silica etc. 
什么是金属键(metallic bonds)?
In a metal lattice, valence electr*** are loosely attached by the nuclei of metal atoms. Thus, valence electr*** require very low energy to release themselves from nuclei. Once these electr*** detach, metal atoms become positively charged i***. These positively charged i*** are surrounded by a large number of negatively charged, free moving electr*** called an electron cloud. Electrostatic forces are formed due to the attracti*** between the electron cloud and i***. These forces are called metallic bonds. In metallic bonds, almost every atom in the metal lattice shares electr***; so there is no way to determine which atom shares which electron. Because of this reason, electr*** in metallic bonds are referred to as delocalized electr***. Due to the free moving electr***, metals are known for good electricity conductors. Examples of metals with metallic bonds include iron, copper, gold, silver, nickel etc.
离子共价(ionic covalent)和金属键(metallic bonds)的区别
定义
离子键:离子键是在负离子和正离子之间产生的静电。
共价键:共价键是当两个元素共享一个价电子以获得中性气体的电子构型时形成的键。
金属键:金属键是带负电的****电子和带正电的金属离子之间的作用力。
键能
离子键:键能高于金属键。
共价键:键能高于金属键。
金属键:键能低于其他主键。
形成
离子键:当一个原子向另一个原子提供电子时形成的离子键。
共价键:两个原子共用价电子时形成共价键。
金属键:当一个金属晶格中有可变数量的原子共享可变数量的电子时,金属键就形成了。
导电性
离子键:离子键的导电性很低。
共价键:共价键的导电率很低。
金属键:金属键具有很高的导电性和导热性。
熔点和沸点
离子键:离子键具有较高的熔点和沸点。
共价键:共价键具有较低的熔点和沸点。
金属键:金属键具有高熔点和沸点。
物理状态
离子键:离子键只存在于固态。
共价键:共价键以固体、液体和气体的形式存在。
金属键:金属键只以固体的形式存在。
债券性质
离子键:这种键是非定向的。
共价键:键是定向的。
金属键:键是非定向的。
硬度
离子键:由于晶体结构,离子键很硬。
共价键:除了金刚石、硅和碳,共价键不是很硬。
金属键:金属键不是很硬。
延展性
离子键:具有离子键的材料不可延展。
共价键:具有共价键的材料是不可延展的。
金属键:具有金属键的材料具有延展性。
延展性
离子键:具有离子键的材料不具有延展性。
共价键:具有共价键的材料不具有延展性。
金属键:具有金属键的材料具有延展性。
示例
离子键:例如LiF、NaCl、BeO、CaF2等。
共价键:例如氢气、氮气、水分子、金刚石、二氧化硅等。
金属键:例如铁、金、镍、铜、银、铅等。
参考文献:
Cracolice, Mark. Basics of Introductory Chemistry with Math Review. 第2版,n.p.:cengage learning,2009,印刷版。
Duke, Catherine Venessa. A., and Craig Denver Williams. Chemistry for Environmental and Earth Sciences. n、 页:华润出版社,2007年出版。
Garg, S. K. Comprehensive Workshop Technology. n、 p.:laxmi出版物,2009年。印刷。
Image Courtesy:
“Ionic Bonds” By BruceBlaus – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0)通过Comm*** Wikimedia
“Covalent Bonds” By BruceBlaus – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0)通过Comm*** Wikimedia
“Metallic bonding” By Muskid – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) 通过Comm*** Wikimedia
- 发表于 2021-06-28 11:41
- 阅读 ( 810 )
- 分类:科学
你可能感兴趣的文章
共价有机物(covalent organic)和金属有机骨架(metal organic framework)的区别
...维或三维有机固体。它是一类含有与有机配体配位的金属离子或簇合物的固体化合物。这是配位聚合物材料的一个子类。这种材料的特点是其多孔结构。这些结构中的有机配体有时被称为“支柱”。 金属有机骨架是一种与具有...
- 发布于 2020-09-20 23:39
- 阅读 ( 400 )
共价半径(covalent radius)和金属半径(metallic radius)的区别
...之间距离的一半,而金属半径是金属结构中两个相邻金属离子之间距离的一半。 共价半径和金属半径都是原子核之间距离的一半;在共价半径中,我们认为同一化学元素的原子之间只有一个共价键,而在金属半径中,我们考虑...
- 发布于 2020-10-16 21:04
- 阅读 ( 746 )
共价键(covalent bond)和与格键(dative bond)的区别
...电负性值相近的非金属原子之间,或电子与带正电的金属离子之间。 图01:两个氢原子之间共价键的形成 共价键主要有两种类型:极性键和非极性键。两个原子之间存在极性键,它们的电负性值相差在0.4到1.7之间。如果这个差...
- 发布于 2020-10-17 17:57
- 阅读 ( 844 )
电价的(electrovalent)和共价键(covalent bond)的区别
...的化合物。化学键有三种主要类型,即离子键、共价键和金属键或非共价键。 内容1。概述和主要区别2。什么是电价键3。什么是共价键4。并排比较-电价与共价键5。摘要 什么是价键(an electrovalent bond)? 价键或离子键是电子从一...
- 发布于 2020-10-23 11:30
- 阅读 ( 343 )
共价(covalent)和非共价债券(noncovalent bonds)的区别
...任何电子而形成的。 化学键主要有四种类型:共价键、离子键、氢键和范德华相互作用。当我们把化学键分为共价键和非共价键时,离子键、氢键和范德华相互作用都属于非共价键的范畴。 目录 1. 概述和主要区别 2. 什么是共...
- 发布于 2020-10-23 12:39
- 阅读 ( 458 )
离子键合(ionic bonding)和金属键合(metallic bonding)的区别
离子键合和金属键合的关键区别在于,离子键合发生在正离子和负离子之间,而金属键合发生在正离子和电子之间。 正如美国化学家G.N.Lewis所说,当原子的价壳层中含有8个电子时,原子是稳定的。大多数原子的价壳层中的电...
- 发布于 2020-10-24 01:03
- 阅读 ( 852 )
离子型(ionic)和共价化合物(covalent compounds)的区别
离子型(ionic)和共价化合物(covalent compounds)的区别 根据离子和共价化合物在水中的溶解度、电导率、熔点和沸点等宏观性质,可以注意到它们之间的许多差异。造成这些差异的主要原因是它们的结合方式不同。因此,它们的键...
- 发布于 2020-10-24 16:55
- 阅读 ( 489 )
离子型(ionic)和共价键(covalent bonds)的区别
离子键和共价键之间的关键区别在于,离子键发生在电负性非常不同的原子之间,而共价键发生在电负性差异相似或极低的原子之间。 正如美国化学家G.N.Lewis提出的那样,当原子的价壳层中含有8个电子时,原子是稳定的。...
- 发布于 2020-11-05 20:46
- 阅读 ( 464 )
离子共价(ionic covalent)和氢化物(metallic hydrides)的区别
离子共价和金属氢化物之间的关键区别在于它们的形成。当氢与高电正性s-块元素反应时形成离子氢化物;当具有可比电负性值的化学元素的原子与氢反应时形成共价氢化物,而当过渡金属与氢反应时形成金属氢化物。 氢化...
- 发布于 2021-03-04 17:20
- 阅读 ( 426 )
非极性(non-polar)和极性共价键(polar covalent bonds)的区别
...于极性的三类,也属于共价键的两类。所有这三种类型(离子、极性和非极性)都被归类为化学键,其中有一种力(电负性)允许两种特定元素的原子相互吸引。可能的共价键的数目由特定元素的电子外壳中空位的数目决定。 ...
- 发布于 2021-06-24 05:05
- 阅读 ( 606 )